How RAG Works: Build Semantic Search with Vectors
Nov 28, 2025
Learn how RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) uses vector embeddings to power semantic search and AI-driven insights from large datasets.

When faced with managing vast repositories of documents and ensuring seamless access to critical information, intellectual property (IP) professionals encounter a formidable challenge: How can large-scale document data be efficiently searched and utilized to support decision-making? The concept of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) offers a transformative solution. This innovative framework integrates retrieval systems with AI-driven natural language generation to provide accurate, context-aware insights - precisely what patent attorneys, inventors, and legal researchers need to streamline their workflows.
In this article, we’ll explore what RAG is, how it works, and why IP professionals should take notice. By the end, you’ll understand how to leverage this approach to enhance your document management strategies and improve efficiency.
What Is RAG and Why Does It Matter?
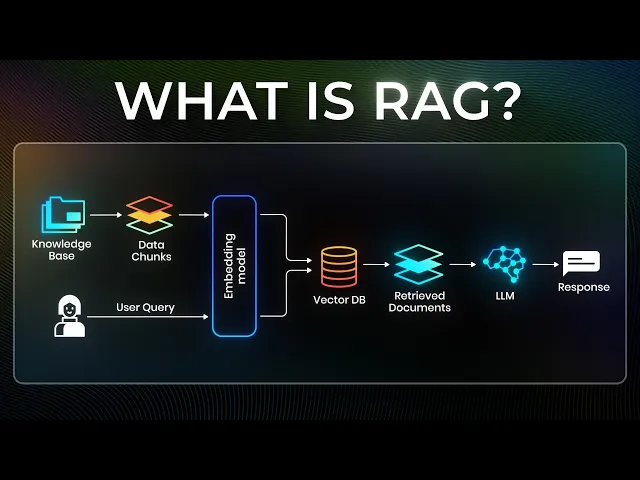
RAG, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation, merges two powerful techniques: semantic search and AI-driven natural language generation. Rather than relying on keyword-based searches or entirely static pre-trained AI models, RAG enables dynamic interactions with your organization’s private knowledge base to provide accurate and contextually relevant answers.
Here’s why this is groundbreaking for IP professionals managing large data sets such as patent filings, legal briefs, or prior art databases:
Efficiency: RAG avoids the inefficiencies of searching massive repositories by pre-processing and storing data in a structured, retrievable format.
Accuracy: Unlike static AI models, which may lack up-to-date information, RAG dynamically pulls the most relevant and current data during runtime.
Customization: The system adapts to the specific needs of your organization, supporting diverse document types and formats.
If you’ve ever struggled with extracting key insights from gigabytes of complex legal documentation, RAG offers a smarter, more scalable solution.
Breaking Down RAG: A Three-Step Process
RAG operates through three core steps: Retrieval, Augmentation, and Generation. Let’s dive into each stage to understand how they work together.
1. Retrieval: The Power of Semantic Search
At the heart of RAG is semantic search, which focuses on meaning rather than just keywords. This is a major leap forward for professionals handling nuanced legal and technical language, where context is crucial.
Here’s how it works:
Documents are pre-processed into vector embeddings, which convert words into numerical representations based on semantic meaning.
When a query is made (e.g., "What clauses are included in last year’s contract with Company X?"), it is also converted into a vector.
The system then compares the query vector to document vectors in a vector database, retrieving the most relevant matches based on context rather than exact word matches.
For example, phrases like "intellectual property protection" and "patent safeguards" might generate similar results, capturing the underlying meaning.
2. Augmentation: Enriching AI with Real-Time Data
Traditional AI models often rely solely on static, pre-trained knowledge, which can quickly become outdated or irrelevant for specialized fields like intellectual property. Augmentation solves this issue by injecting real-time, context-specific data into the AI’s prompt at runtime.
When a query is submitted, the retrieved results from the semantic search are appended to the AI model’s input, creating a context-rich prompt. This ensures the generated response is informed by the most relevant, up-to-date, and private information available in your organization’s database.
For IP professionals, this means the model can incorporate critical details from documents like:
Patent filings
Licensing agreements
Litigation records
3. Generation: Delivering Human-Like Responses
Finally, the AI uses the augmented prompt to generate a response. This response draws on both the retrieved data and the model’s language capabilities to deliver coherent, context-aware outputs.
For example, if you ask, "What licensing terms apply to Patent X?" the RAG system will:
Retrieve relevant licensing agreements.
Augment the AI model with those agreements.
Generate a detailed answer, specifying key clauses or terms.
The result? Precise, actionable insights that save hours of manual research.
Building a RAG System: Key Strategies
Creating an effective RAG system requires careful consideration of several factors. These include:
Data Chunking
Documents must be split into manageable chunks before being processed into vector embeddings. The size and overlap of these chunks are critical. For example:
Legal documents may require larger chunks (e.g., 500 words) to preserve paragraph-level context.
Conversational transcripts might benefit from smaller chunks with higher overlap to maintain continuity.
Embedding Models
Selecting the right embedding model is crucial for achieving accurate results. In the case study discussed, the all-MiniLM-L6-v2 model was used. This compact and efficient model balances computational efficiency with semantic accuracy.
Retrieval Strategies
Fine-tuning retrieval parameters, such as similarity thresholds, ensures that only the most relevant results are surfaced. This reduces noise and avoids the risk of hallucination (i.e., the generation of incorrect or low-quality responses).
Practical Applications for IP Professionals
RAG is particularly well-suited to the demands of intellectual property work, where precision and context are non-negotiable. Here are just a few ways this approach can be applied:
Patent Search and Analysis:
Retrieve relevant prior art based on semantic meaning, not just keywords.
Answer complex questions about patent claims or classifications using real-time data.
Contract Review:
Quickly locate and summarize specific clauses in licensing agreements or service contracts.
Ensure compliance by cross-referencing terms with internal policies.
Litigation Support:
Access key case law or precedents from a private database of legal records.
Generate summaries or insights tailored to the specifics of an ongoing case.
Collaboration Across Teams:
Facilitate seamless knowledge sharing by creating a centralized, searchable knowledge base.
Support legal and technical teams simultaneously with accurate, domain-specific answers.
Key Takeaways
RAG combines semantic search with AI-driven response generation, enabling accurate and efficient document retrieval.
Semantic search focuses on meaning rather than keywords, making it ideal for handling complex, context-rich data such as patents or legal agreements.
Augmentation ensures AI models remain up-to-date, incorporating organization-specific data during runtime without requiring extensive fine-tuning.
Customizable chunking and embedding strategies allow RAG systems to adapt to diverse document types and workflows.
For IP professionals, RAG provides actionable insights for tasks like patent research, contract analysis, and litigation support.
Conclusion
The ability to retrieve, augment, and generate insights from vast document repositories isn’t just a technological advancement - it’s a game-changer for intellectual property professionals. By implementing a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system, patent attorneys, inventors, and legal teams can overcome the inefficiencies of traditional search systems, ensure up-to-date answers, and unlock the full potential of their document archives.
With the increasing complexity of IP landscapes, the time to explore and adopt RAG is now, ensuring that your team stays ahead in the race for precision and efficiency. The future of document search isn’t just about finding information - it’s about transforming it into actionable knowledge.
Source: "RAG Explained For Beginners" - KodeKloud, YouTube, Aug 13, 2025 - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_HQ2H_0Ayy0