
Vector AI for Patent Claim Similarity
Intellectual Property Management
Sep 9, 2025
Vector AI revolutionizes patent analysis by transforming claims into semantic vectors, enhancing accuracy in searches, drafting, and infringement assessments.

Patent professionals often struggle with analyzing patent claims due to the limitations of traditional keyword searches. Vector AI changes the game by converting patent claims into mathematical vectors that capture their semantic meaning, enabling more precise comparisons. This approach improves tasks like prior art searches, claim drafting, and infringement analysis by focusing on concepts rather than just keywords.
Key Points:
What it does: Transforms patent claims into numerical vectors to analyze meaning and relationships.
Why it matters: Helps identify similar claims for better prior art searches, stronger patents, and reduced legal risks.
How it works: Uses embedding models (e.g., Word2Vec, Doc2Vec, BERT) trained on patent data to generate detailed vector representations.
Accuracy: Depends on training quality, dataset diversity, and handling of complex patent language.
Applications: Enhances patent searches, supports infringement analysis, and aids competitive evaluations.
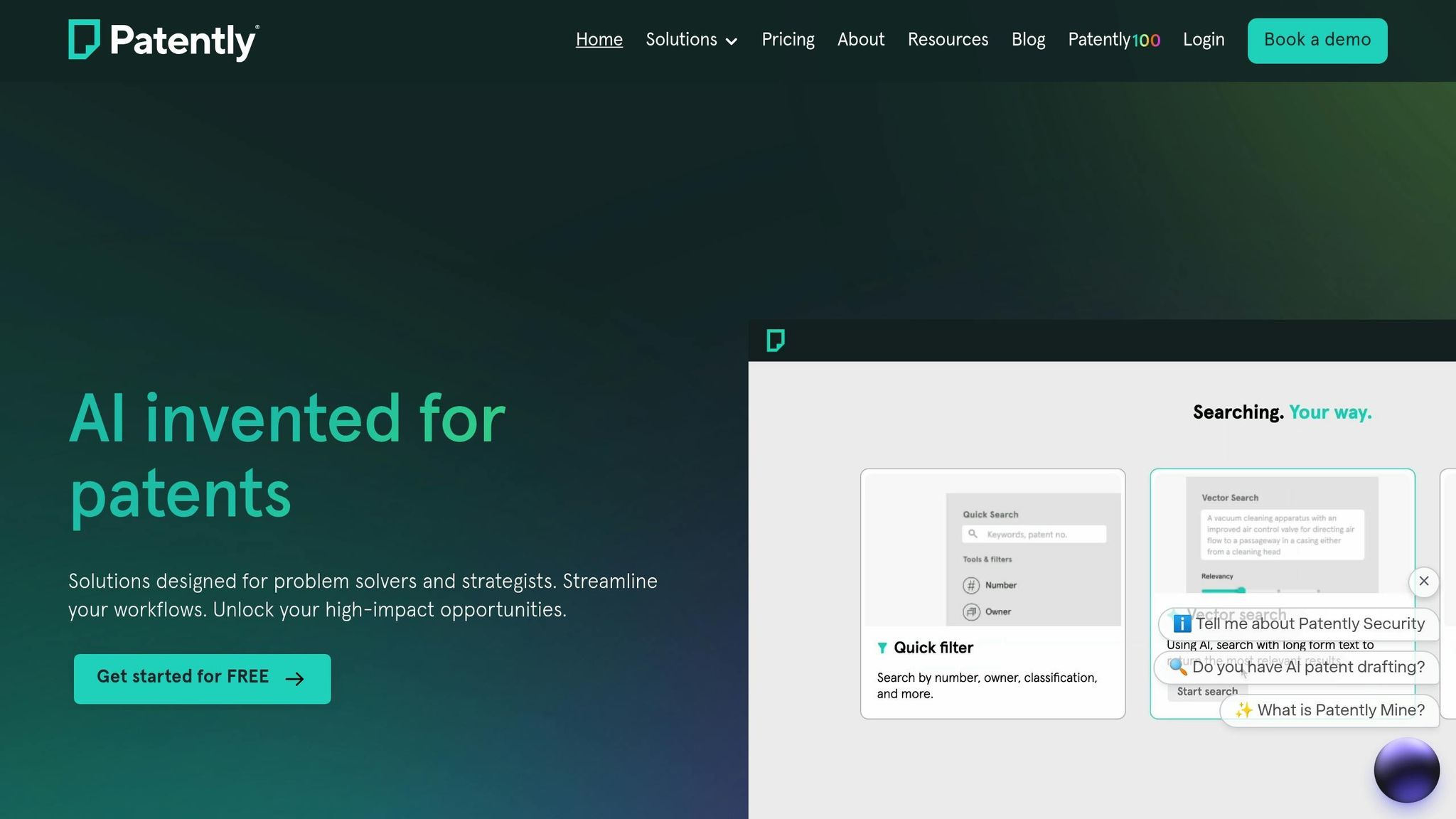
Quick Insight: Vector AI tools like Patently and Garden are reshaping patent workflows by automating complex tasks, improving efficiency, and reducing costs.
Patently: How to guides... Vector search
Embedding Techniques for Patent Claim Similarity
The success of using Vector AI in patent analysis largely hinges on the embedding techniques that convert patent claims into numerical data. These techniques have come a long way, with various models offering tailored benefits for professionals aiming to compare claims with precision.
Common Embedding Models
Different embedding models bring unique strengths to the table when analyzing patent claims. Word2Vec is one of the earliest approaches, creating vector representations by examining word relationships within patent datasets. While it captures basic word meanings, it struggles with the complexity of long, detailed patent claims.
Doc2Vec takes things further by generating embeddings for entire documents instead of focusing on individual words. For patent claims, this model provides a more comprehensive view, preserving the full context of a claim rather than breaking it into smaller pieces. This makes it easier to compare claims as a whole.
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) has set a new standard in patent analysis by interpreting context in both directions of a sentence. Unlike older models that process text sequentially, BERT analyzes the entire claim at once. This allows it to pick up on nuanced relationships between technical terms and their meanings within specific contexts.
Specialized models trained solely on patent data offer even greater accuracy. These domain-specific models are fine-tuned to understand the unique language, terminology, and structure of patent claims. For example, they recognize that phrases like "comprising", "consisting of", or "wherein" carry distinct legal implications in patent documents, differing from their everyday use.
Using these models, the process of transforming patent claims into precise vector representations becomes highly effective.
How Models Convert Patent Claims to Vectors
Embedding models translate the text of a patent claim into numerical values that reflect its meaning. Each word or phrase is mapped to coordinates in a high-dimensional space - often with hundreds of dimensions. These coordinates are carefully positioned based on the semantic relationships the model has learned.
For instance, when analyzing a claim like "a mobile device comprising a processor and memory", the model doesn’t just process individual words. It understands that "mobile device" refers to portable electronics, "comprising" indicates an open-ended claim structure, and "processor and memory" imply computational capabilities. The resulting vector captures these relationships in mathematical form.
By training on millions of patents, the model learns patterns in how technical terms are used together. For example, it might recognize that patents mentioning "wireless communication" are often associated with terms like "antenna", "signal processing", or "network connectivity."
The use of high-dimensional vectors allows for detailed and nuanced representations. A 300-dimensional vector, for example, can distinguish between patents that both involve "wireless communication" but differ in focus - one on cellular networks, the other on Wi-Fi protocols. These detailed representations form the foundation for accurate similarity measurements.
Once the claims are represented as vectors, mathematical techniques are used to measure their similarities.
Measuring Similarity: Cosine Similarity and Other Methods
After converting patent claims into vectors, comparing their similarity involves mathematical methods designed to analyze relationships in high-dimensional space. One of the most commonly used techniques is cosine similarity, which measures the angle between two vectors rather than their distance. This approach emphasizes the direction of the vectors, making it ideal for capturing conceptual similarities.
Cosine similarity produces scores ranging from -1 to 1. Scores above 0.8 typically indicate strong similarity, while those below 0.3 suggest little to no relation. These scores give patent professionals clear metrics for evaluating how closely claims are related.
Another method, Euclidean distance, measures the straight-line distance between vectors in the high-dimensional space. While less popular than cosine similarity, it can be useful in scenarios where the absolute size of vector components is important. Some systems combine both cosine similarity and Euclidean distance to offer a more rounded analysis.
Manhattan distance provides another option by summing the absolute differences between vector components. This method is particularly helpful for identifying patents that share specific technical elements, even if their broader approaches differ.
For deeper insights, advanced methods like Jaccard similarity and semantic similarity scores come into play. These techniques can identify patents with shared technical elements or legal structures, even when their overall vector representations differ. By using a mix of these similarity metrics, patent professionals can gain a well-rounded view of claim relationships, helping them make informed decisions about strategies and potential risks.
Accuracy of Vector AI in Patent Analysis
When it comes to analyzing patent claims, accuracy is everything. While embedding techniques are the foundation, evaluating how well Vector AI performs in identifying claim similarities is what really determines its reliability in practical applications. Several key factors come into play when assessing the model's performance.
Factors That Affect Model Accuracy
The accuracy of Vector AI in patent claim analysis hinges on a mix of technical and contextual elements, including:
Domain-specific training: Tailored training helps the model handle specialized legal terms and technical jargon more effectively.
Quality and diversity of datasets: A well-rounded dataset representing various technical fields ensures consistent and reliable outcomes.
Complexity of patent language: Simpler claims tend to yield more accurate similarity assessments compared to highly intricate ones.
Terminology variations: Differences in wording due to document age or translations can challenge the model's ability to identify similarities across time periods or languages.
Preprocessing techniques: Proper preprocessing sharpens the quality of vector representations, directly impacting the model's performance.
These factors collectively shape how well Vector AI performs in patent analysis tasks.
Research Results and Benchmarks
Research highlights that Vector AI performs particularly well in domains where standardized language is the norm. For example, when patent claims revolve around shared technical concepts, the model tends to deliver high similarity scores. On the other hand, claims with only surface-level similarities are appropriately assigned lower scores. This consistency is especially evident in fields with uniform terminology and structure.
Benefits and Limitations of Current Methods
Vector AI brings several advantages to the table when analyzing patent claims:
Speed: It processes large volumes of patent claims quickly, saving significant time compared to manual reviews.
Consistency: By reducing variability in assessments, it offers a more standardized evaluation process.
Nuance detection: The model can uncover subtle relationships between patents that might escape traditional analysis.
However, there are still hurdles to overcome. For instance, the model sometimes struggles with understanding the context and legal subtleties embedded in patent claims. Additionally, biases in the training data and the computational demands of analyzing extensive patent portfolios remain significant challenges. These limitations highlight areas where further refinement is needed to enhance its reliability.
Vector AI Applications in Patent Management
Vector AI is reshaping patent management by making searches faster and analyses more efficient. From speeding up prior art searches to aiding infringement investigations, this technology is creating noticeable improvements throughout the patent lifecycle. Below, we’ll explore its impact on patent search, claim drafting, and competitive analysis.
Improving Patent Search and Claim Drafting
Vector AI enhances prior art searches by converting patent documents into precise vector formats. Unlike traditional keyword-based searches, this approach identifies related concepts with greater accuracy. For instance, a search for "wireless communication device" might also surface patents mentioning "mobile phone", "cellular handset", or "portable communication apparatus", thanks to the technology's ability to understand conceptual relationships.
When it comes to claim drafting, Vector AI provides patent attorneys with a powerful tool to identify existing claims that share similar scope and structure. This helps in crafting stronger, more defensible claims. By analyzing millions of patents in seconds, AI tools can deliver insights that would take human reviewers weeks to compile. Additionally, these tools can generate claim-chart-quality analyses in just minutes, significantly reducing both review time and costs.
Supporting Infringement and Competitive Analysis
Vector AI plays a significant role in detecting patent infringement with remarkable speed and accuracy. By comparing millions of patent–product pairings in seconds, it brings a level of efficiency that manual methods simply can’t match. It also aids in competitive patent landscape evaluations, automating the analysis of large patent datasets to uncover potential conflicts, assess competitor patents, and perform detailed freedom-to-operate analyses.
A standout example of this technology in action is Garden, a New York-based startup. They expanded their searchable patent database from 20 million to over 200 million patents. At the same time, they improved query latency, cutting it from 250–400 milliseconds to under 100 milliseconds. Costs per stored gigabyte were slashed by a factor of 10. By implementing filterable HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World), Garden launched a full infringement-analysis product, opening new business opportunities. These advancements not only improve infringement detection but also support more robust patent strategies across the lifecycle.
Vector AI also helps identify prior art to challenge patent validity or defend against infringement claims. Large Language Models trained on extensive patent and technical literature can generate detailed reports, pointing out weaknesses in patent claims and suggesting areas where prior art might exist.
Integration with AI-Powered Platforms like Patently
The benefits of Vector AI are amplified when integrated into platforms like Patently, which streamline the patent workflow. Patently uses Vector AI to enhance search, drafting, and Standard Essential Patent (SEP) analytics. These platforms combine advanced semantic search with AI-driven drafting and analytics tools, maximizing the potential of vector-based technologies.
Patently’s semantic search goes beyond keyword matching, using Vector AI to find patents based on conceptual similarities - a major advantage when navigating complex technical fields. Its AI-powered drafting assistant, Onardo, leverages vector-based insights to help attorneys create stronger patent applications by analyzing existing patents and identifying coverage gaps.
For SEP analytics, Patently uses Vector AI to examine the relationships between patents and technical standards. This helps businesses understand their position in standards-based markets and identify licensing opportunities or risks. Additionally, the integration of Vector AI in patent management platforms supports thorough validity checks before acquiring or licensing patents, ensuring investments in intellectual property are well-founded and enforceable.
These applications highlight how Vector AI is no longer just an emerging technology - it’s becoming a vital tool in modern patent management, driving improvements in speed, precision, and cost-efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Vector AI has reshaped how patent professionals evaluate claim similarities, turning what used to be tedious, manual tasks into more efficient processes. By grasping conceptual relationships rather than relying solely on keyword matches, it has unlocked new opportunities in patent searches, drafting, and competitive analysis. These advancements are directly improving both day-to-day operations and long-term strategies.
Benefits of Vector AI
With its advanced embedding techniques, Vector AI makes analyzing patent claims faster and more efficient. Patent professionals can now handle massive datasets quickly, cutting down on both time and storage costs.
It also brings a new level of precision. Unlike traditional keyword-based searches, Vector AI identifies patents with similar concepts, even when the language differs. This expands the scope of prior art searches and strengthens infringement analyses.
The technology speeds up decision-making throughout the patent lifecycle. Whether drafting a new patent, challenging validity, or negotiating licensing agreements, Vector AI delivers timely insights that help attorneys make better strategic choices. Tools like Patently integrate these features directly into patent workflows, making them even more accessible.
Future Trends in AI-Powered Patent Management
The future of Vector AI in patent management looks even more promising. Enhanced embedding models tailored specifically for patent language are already boosting accuracy. Real-time patent monitoring is also gaining traction, allowing the technology to continuously scan new filings for potential conflicts or opportunities. This means companies can quickly respond to competitive challenges and spot licensing opportunities as they arise.
Another emerging trend is broader integration. Vector AI is starting to link patent data with trademark databases, technical standards, and market insights. This interconnected approach gives patent professionals a more complete view of the innovation and competitive landscape.
Looking ahead, predictive analytics is set to be a game-changer. Beyond finding similar patents, Vector AI is beginning to predict outcomes like prosecution results or infringement risks. This shift toward forecasting will make patent management even more data-driven and strategic.
FAQs
How does Vector AI enhance the accuracy of patent claim analysis compared to traditional keyword searches?
Vector AI transforms patent claim analysis by prioritizing semantic meaning and contextual relationships over simple keyword matching. By embedding patent claims into high-dimensional vectors, it can detect similarities even when different terms or phrases are used, offering a deeper and more precise understanding of the content.
This method significantly cuts down on irrelevant results and false positives, streamlining the process of identifying genuinely similar patents and claims. Studies highlight that embedding techniques such as Doc2Vec and BERT-based models achieve much higher accuracy and dependability compared to traditional keyword-driven approaches.
What challenges does Vector AI face in measuring patent claim similarity, and how can they be resolved?
Vector AI encounters several hurdles when it comes to evaluating patent claim similarity. One key challenge is semantic ambiguity - small variations in wording or phrasing can result in significant differences in interpretation. Another difficulty lies in creating embeddings that effectively capture the intricate and highly technical details found in patent claims. Moreover, the presence of multilingual and domain-specific terminology adds another layer of complexity, often compromising the accuracy of similarity assessments.
To tackle these issues, embedding techniques can be fine-tuned through domain-specific training and incorporating multilingual models. Additionally, refining algorithms to better grasp the technical and contextual subtleties of patent claims can lead to more precise results. These improvements aim to provide patent professionals with more dependable and accurate tools for their work.
How do AI models like BERT and Doc2Vec help analyze complex patent language?
AI models like BERT and Doc2Vec are transforming the way complex patent language is analyzed. By focusing on the meaning and context of words and phrases within technical and legal texts, these tools bring a new level of precision to understanding intricate documents.
BERT, with its deep learning architecture, is particularly skilled at grasping subtle terminology and the relationships between words in a sentence. This makes it highly effective for interpreting the often-complicated language found in patent claims.
On the other hand, Doc2Vec takes a broader approach by creating dense vector representations of entire documents. This allows it to capture the overall context and structure of lengthy patent texts. Thanks to these strengths, both models enable more accurate comparisons, enhance semantic search, and improve the classification of patent claims - ultimately simplifying the analysis process for patent professionals.