
How Vector AI Improves Multilingual Patent Search
Intellectual Property Management
Aug 6, 2025
Vector AI enhances multilingual patent searches by focusing on meaning, improving accuracy and efficiency in identifying relevant documents across languages.

Vector AI is transforming patent searches by focusing on meaning rather than exact words. It uses semantic embeddings to understand the intent behind patent documents, making it easier to find related patents across languages. Here's why this matters:
Traditional Challenges: Keyword searches struggle with language differences, synonyms, and technical terms, often missing key patents or delivering irrelevant results.
How Vector AI Works: It converts text into numerical vectors, grouping similar concepts together, regardless of language or terminology.
Benefits:
Speeds up research by processing millions of records in minutes.
Improves accuracy with meaning-based search, reducing missed patents.
Simplifies global patent management with multilingual capabilities.
Recent advancements, like models from Google DeepMind and the European Patent Office, further enhance the precision of these searches. Tools like Patently already use these technologies to deliver faster, more accurate results for patent professionals.
Semantic Embeddings for Multilingual Patent Retrieval
Understanding Semantic Embeddings
Semantic embeddings are at the heart of modern multilingual patent search, transforming text into numerical vectors. These vectors essentially act as a mathematical representation of meaning, allowing vector similarity to serve as a stand-in for semantic similarity. This approach makes it possible to transcend language barriers in patent research.
Fine-tuned models generate dense vectors that capture the subtle nuances of patent texts. By tapping into natural language processing (NLP), semantic embeddings go beyond simple translations, capturing the intent behind a search query. For example, an English patent on "wireless communication" will produce a vector that aligns closely with a German patent on "drahtlose Kommunikation" or a Japanese patent discussing the same concept. This language-neutral method eliminates many of the challenges traditionally associated with cross-border patent research.
These embeddings also use contextualized approaches to understand the intent behind search queries. This means they can retrieve patents with related ideas, even when different words or languages are used. This numerical representation forms the backbone for exploring advanced embedding models.
Latest Embedding Models
The development of embedding models has advanced rapidly, with multilingual capabilities now being a standard feature. Modern models can handle over 100 languages in a single vector space, significantly improving the precision of cross-lingual patent retrieval.
Some standout models include:
SEARCHFORMER: Developed by the European Patent Office in 2023, this patent-specific BERT model outperforms traditional keyword extraction methods and even general-purpose SentenceTransformer models.
Gemini Embedding by Google DeepMind: Achieves a Mean MTEB score of 68.3, showcasing its strong multilingual performance.
voyage-3-large from Voyage AI: Outpaces competitors by 9.74%–20.71%, emphasizing its edge in accuracy.
Multilingual-E5-large: Supports nearly 1,000 languages, pushing the boundaries of cross-lingual capabilities.
Trends in this space include embedding models tailored for specific domains like legal and technical texts, as well as instruction-tuned embeddings that adapt dynamically based on natural language prompts. These advancements highlight how semantic embeddings are reshaping multilingual patent retrieval, creating opportunities for more precise and efficient research.
Benefits of Semantic Similarity
Semantic similarity offers a clear advantage over traditional keyword-based searches when it comes to cross-lingual patent retrieval. Unlike keyword searches, which rely on exact matches or predefined synonyms, semantic embeddings grasp the conceptual relationships between terms, even across languages and technical fields.
For instance, a semantic search can identify patents related to "artificial intelligence methods", "neural network architectures", or "pattern recognition systems", regardless of the language used. This deeper understanding significantly improves recall and minimizes the risk of missing critical prior art.
Additionally, large language models can generate detailed descriptions to help interpret patent images and diagrams. This extension of semantic search beyond text enhances the overall search experience, making it more comprehensive.
With improved recall capabilities, patent professionals can uncover relevant prior art that might otherwise be missed with traditional keyword-based methods. By bridging gaps in technical vocabularies, regional terminology, and industry-specific language, semantic similarity is revolutionizing global patent research. These innovations empower platforms like Patently to deliver precise, cross-border patent insights with greater efficiency and accuracy.
Vector Search Algorithms and Large-Scale Retrieval
How Vector Search Works
Vector search algorithms bring the power of semantic embeddings to multilingual patent retrieval. By transforming patent texts into semantic embeddings, these algorithms enable similarity-based searches across languages using approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) methods rather than traditional keyword matching.
Instead of simply matching keywords, the algorithm identifies patents with semantic vectors closest to the query. For instance, if a professional searches for "wireless communication technology", the system retrieves patents with vectors that align closely with the query vector. This approach uncovers relevant documents that might use different terms or phrasing.
Relevance feedback techniques further enhance search precision. The affine vector subspace method refines the original query using feedback from documents marked as relevant. Unlike the Rocchio algorithm - which averages the vectors of relevant documents - the affine subspace method identifies the point in the space spanned by relevant vectors that is closest to the query vector.
Performance in Large-Scale Retrieval
Research highlights impressive performance gains with vector search algorithms in large-scale patent databases. For example, using the affine subspace method with feedback from 10 relevant documents has achieved top-5 recall rates as high as 99.4%, along with improved precision and Mean Average Precision (MAP) scores.
A standout example is the SEARCHFORMER model, tailored specifically for patent language. It uses an evaluation method that tracks the rank of the highest-ranked "X-type" citation - citations that influence novelty or inventive step determinations.
Moreover, the affine subspace method demonstrates strong resilience against noise, which can occur when multiple relevant documents belong to the same patent class. These advancements showcase how vector search can address complex retrieval challenges, especially in large-scale settings.
Scalability Challenges and Solutions
Handling millions of multilingual patent records introduces significant scalability barriers. One major issue is the sheer computational complexity and memory demand. For example, storing a billion 768-dimensional vectors requires approximately 3 TB of memory. This makes exact nearest neighbor search infeasible for such large datasets. The high-dimensional nature of these vectors also increases the computational load for distance calculations, and real-time updates or high query throughput add further strain.
To tackle these challenges, several strategies are employed to ensure scalability without compromising performance:
Scalability Strategy | Implementation | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) | Balances slight accuracy loss for faster searches | Enables real-time queries on massive datasets |
Distributed Systems | Spreads data across multiple nodes | Overcomes memory limits and boosts parallel processing |
Hybrid Storage | Uses memory for frequent queries, disk for less-used data | Optimizes costs while maintaining performance |
While data partitioning helps manage scalability, it introduces challenges in maintaining consistency across distributed systems. Efficient indexing methods - like tree-based or graph-based structures - accelerate the search process. Tools such as FAISS or Milvus are commonly used to address these issues but require careful tuning to fit specific workloads.
Balancing shard sizes and optimizing communication between nodes is another critical aspect. Patent platforms also benefit from caching mechanisms and dynamic cloud-based solutions that scale with search demand. Unlike traditional relational databases, vector databases are purpose-built for handling large-scale, high-dimensional data, making them ideal for semantic search where results are based on meaning rather than exact matches.
Patently: How to guides... Vector search
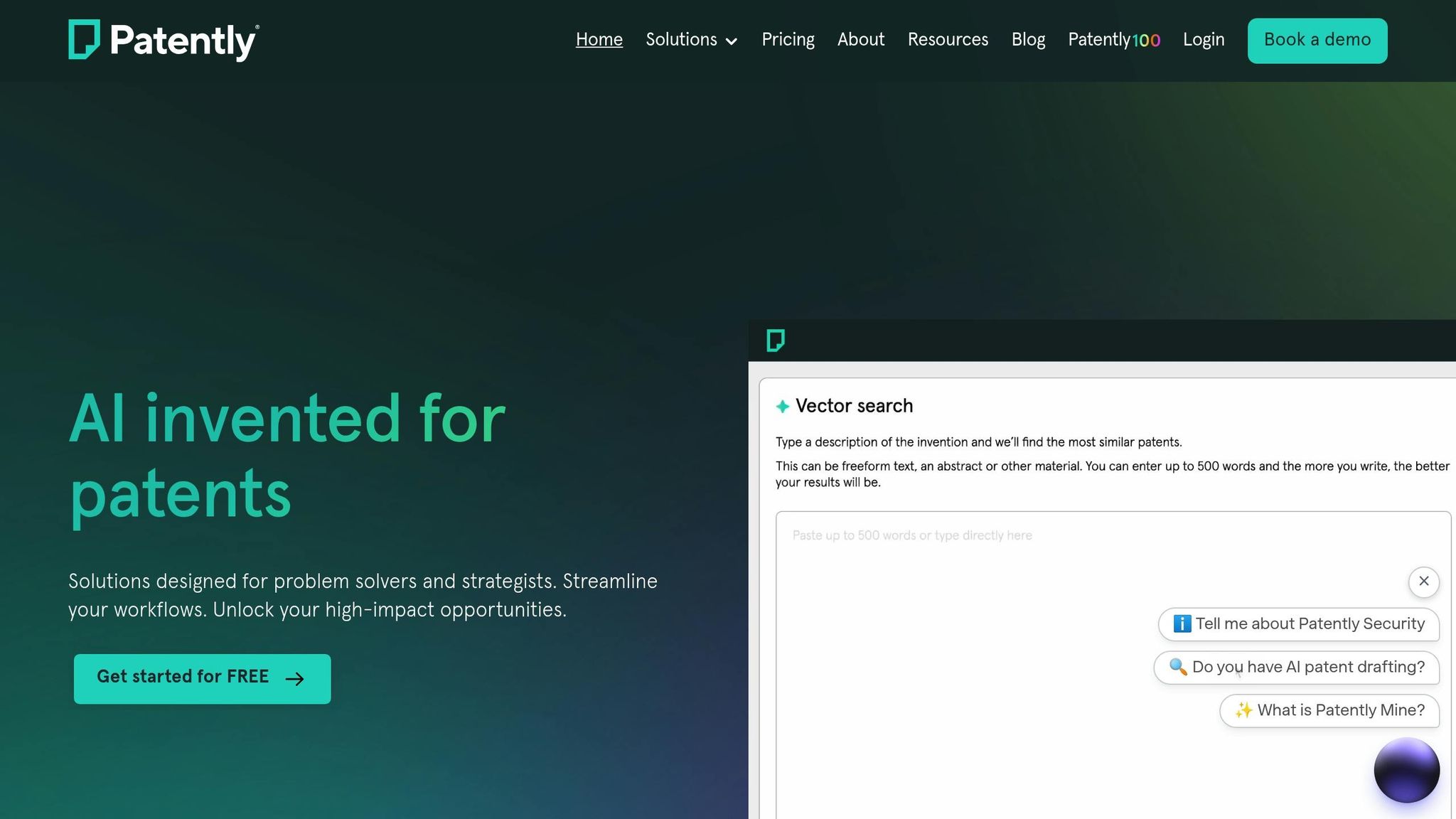
Practical Benefits for Patent Professionals
Vector AI brings a new level of efficiency to multilingual patent searches, offering tools that enhance prior art discovery, improve patent identification, and simplify global patent management.
Better Prior Art Discovery
Traditional keyword searches often fall short because they rely on exact matches, which can overlook critical prior art. Vector AI changes the game by identifying semantically related documents, even when the wording or terminology differs. This means conceptually similar inventions can be uncovered, regardless of the language used. With multilingual vector models, patent professionals can analyze foreign legal texts without being limited to translated metadata. This approach not only removes the delays caused by translation but also ensures that subtle nuances in the original text are preserved.
More Accurate Patent Identification
One of the biggest hurdles in traditional search systems is their inability to understand terms in context. Vector AI addresses this by converting patent texts into numerical data that captures their semantic meaning. This allows researchers and lawyers to find relevant documents even when different terminology is used. For instance, a search for "pool" might miss a patent for "swimming pool" in older systems, but Vector AI bridges this gap by recognizing the underlying connection. This is especially useful for technical patents, where industry-specific or regional language can vary widely. By providing precise results, this technology supports a more comprehensive international patent strategy.
Simplified Global Patent Management
Vector AI also simplifies the complex task of managing patents across multiple languages and jurisdictions. Instead of creating separate search strategies for each language, professionals can perform a single semantic search to locate relevant patents, regardless of their original language. This unified process saves time, minimizes the risk of inconsistent results across jurisdictions, and ensures that international patent applications are well-prepared for global portfolios. Furthermore, when international teams work together on filings or litigation, having access to a unified set of prior art enhances collaboration and reduces redundant efforts.
Vector AI vs. Keyword Search Comparison
Building on the earlier discussion about their technical and practical advantages, let’s dive into a comparison of Vector AI and keyword search. The choice between these methods can determine whether a patent search is thorough or misses critical results. Each approach shines in specific scenarios, especially when dealing with multilingual patent research.
Comparison Table: Vector AI vs. Keyword Search
Feature | Vector AI Semantic Search | Keyword Search |
|---|---|---|
Retrieval Method | Conceptual similarity using embeddings | Exact word/phrase matching |
Language Support | Multilingual, language-agnostic | Language-dependent, often requiring translation |
Efficacy | Excels with nuanced and complex queries | Limited by vocabulary and terminology |
Speed | Real-time and scalable across millions of patents | Slower with large datasets |
Relevance Ranking | Contextual, meaning-based prioritization | Frequency/position-based results |
Handling Synonyms | Captures related concepts effectively | Often misses paraphrases and variations |
Use Case Fit | Ideal for prior art discovery, global search, and novelty assessment | Best for simple, exact term searches |
For instance, Patently's vector search processed 300 relevant patents in under five minutes. This efficiency comes from its ability to evaluate conceptual meaning, making it especially powerful for multilingual searches. By leveraging semantic similarity, Vector AI retrieves relevant patents even when the query and documents use different terminology. These strengths highlight the importance of aligning the search method with the complexity of the task at hand.
When to Use Each Approach
Vector AI is the go-to choice for handling complex, multilingual, and nuanced patent queries. It’s particularly effective for prior art discovery, where inventions might be described differently across countries or technical fields. On the other hand, keyword search is better suited for cases requiring exact matches, such as searching for specific legal terms or standardized phrases.
Ultimately, the decision boils down to your search objectives. If you’re mapping a global patent landscape or conducting a thorough prior art analysis, Vector AI offers the depth needed to uncover patents that keyword searches might miss. However, for targeted searches focused on precise technical specifications or legal language, traditional keyword methods deliver quick and accurate results.
Conclusion and Main Points
Vector AI has redefined the way multilingual patent searches are conducted, turning what was once a manual, labor-intensive process into an automated system that delivers unmatched accuracy and efficiency. By shifting from traditional keyword-based searches to semantic understanding, it addresses major hurdles like language barriers and the complexity of navigating millions of cross-domain documents that have long challenged patent professionals.
Studies reveal that Vector AI can cut time-to-market by 10–20%, reduce development costs by 20–30%, and drive innovation by 30%. These gains are possible because Vector AI focuses on understanding semantic meaning rather than relying solely on exact keyword matches. This makes it a powerful tool for identifying relevant patents across diverse languages and technical fields. The growing importance of such tools is evident in the surge of AI-related patent applications globally, which have grown at an annual rate of over 30% between 2014 and 2023.
With Vector AI, patent professionals now have access to a streamlined, global search process. Tools like Patently offer semantic search capabilities that allow users to efficiently conduct prior art searches, overcome language barriers, and manage international patent portfolios with ease.
FAQs
How does Vector AI improve the accuracy of multilingual patent searches compared to traditional keyword-based methods?
Vector AI improves the accuracy of multilingual patent searches by leveraging semantic embeddings. Unlike basic keyword matching, this technology understands the context and meaning behind terms, even when they're expressed in different languages or phrased differently.
By analyzing the deeper connections between words and ideas, Vector AI delivers more accurate and dependable results. This is particularly valuable in specialized and technical areas like patents. Recent progress in multilingual and domain-specific embeddings has enhanced this functionality, making it an essential tool for patent experts.
What challenges does Vector AI face when scaling for large patent databases, and how are they resolved?
Scaling Vector AI to manage extensive patent databases comes with its fair share of challenges, including fragmented data, restricted language coverage, and intense computational requirements. These hurdles can limit the system’s capability to efficiently process and analyze massive, multilingual datasets.
To tackle these issues, cutting-edge AI-driven vector databases play a key role. These technologies facilitate quicker and more precise semantic searches while offering a nuanced understanding of complex patent information. By fine-tuning algorithms and utilizing scalable infrastructure, Vector AI can seamlessly handle large datasets and deliver real-time insights, even for multilingual patent discovery tasks.
How does Vector AI help patent professionals manage multilingual patent portfolios more effectively?
Vector AI transforms the way multilingual patent portfolios are managed by introducing powerful semantic search tools. These tools allow professionals to locate relevant patent details across various languages and jurisdictions with speed and precision, cutting down on research time while boosting accuracy.
Beyond search capabilities, Vector AI processes massive amounts of patent data to identify trends, detect potential infringements, and aid in making informed strategic decisions. This approach simplifies portfolio management and provides a more efficient way to handle global patent analysis.